How to Uninstall Software Packages on Ubuntu Using apt
This tutorial will guide you through the process of uninstalling packages, including their dependencies and configuration files.
Step 1: Find the Exact Package Name
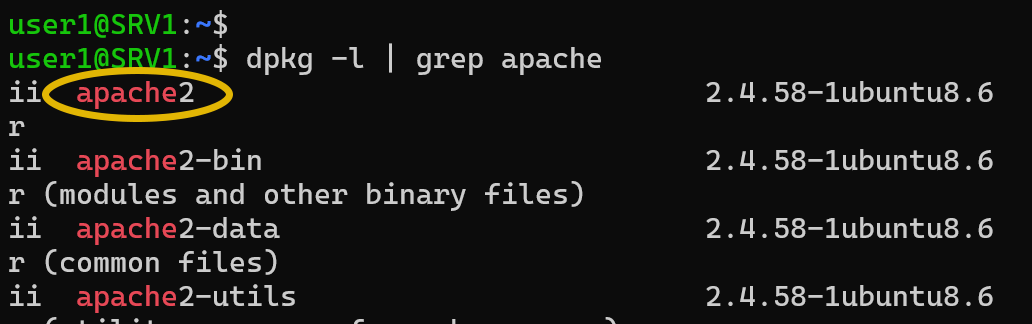
Before you can uninstall a package, you need to know its exact name. You can use the dpkg -l command to list all installed packages.
dpkg -lTo filter the list and find your target package, you can pipe the output to grep. For example, to find the package that provides the Apache web server, run:
dpkg -l | grep apacheStep 2: Remove the Package
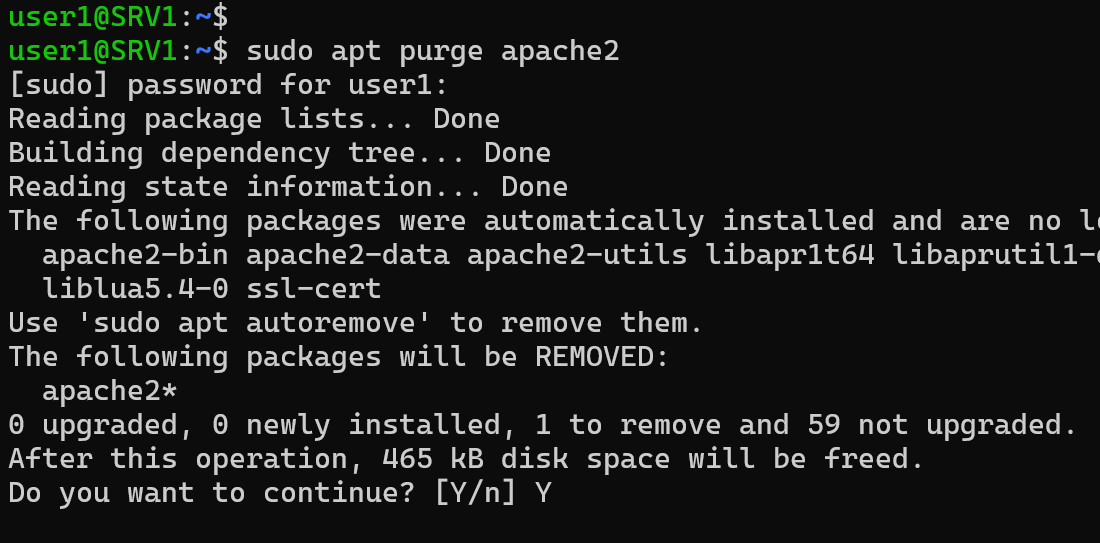
Once you know the package name (for example, apache2), you can remove it using either apt remove or apt purge.
sudo apt purge [package]
sudo apt remove [package]apt removedeletes the package but keeps its config files.apt purgedeletes the package along with its config files.- To completely remove a package, it's generally recommended to use
apt purge.
For example, the following command uninstalls the apache2 package:
sudo apt purge apache2Step 3: Remove Unused Dependencies
After uninstalling a package, some dependency packages may remain. To remove these, use the apt autoremove command:
sudo apt autoremoveThis command removes any dependency packages that are no longer needed by other installed software.
Step 4: Check for Leftover Config Files
Sometimes, apps store user-specific configuration files in the .config directory inside your home folder.
cd ~/.config/This is common with desktop apps like TeamViewer, OBS Studio, or web browsers. These files aren't removed automatically.
You have to remove them manually using the rm command.