How to Clone a WSL 2 Distro (Backup and Restore)
In this tutorial, you will learn how to clone a Linux distribution on Windows Subsystem for Linux 2, which can be useful for creating backups, testing changes, or transferring your environment to another machine.
Click here for instructions on installing WSL 2 if you haven't already.In WSL 2, we use the wsl command to manage Linux distributions. Currently, the wsl command does not directly offer a cloning option for Linux distros. However, there is a simple workaround.
To clone a Linux distribution, first back up the desired distro using the --export option. Then, import the backup to launch a new distro using the --import option. This technique can also be used to migrate a WSL 2 distro from one computer to another.
Command syntax to export WSL 2 distro:
wsl --export <Distro-Name> <File-Name>Command syntax to import WSL 2 distro:
wsl --import <Distro-Name> <Install-Location> <File-Name>Demo
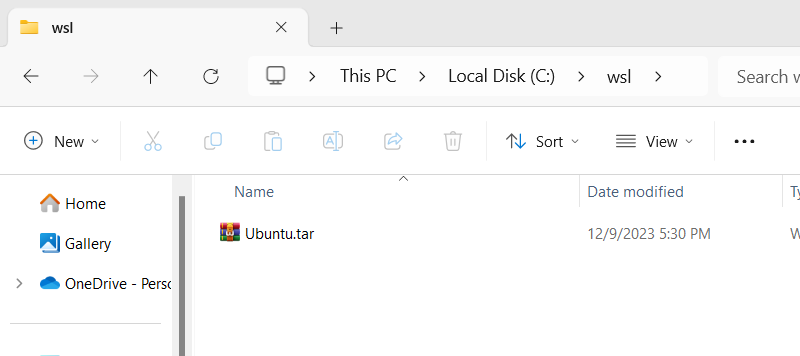
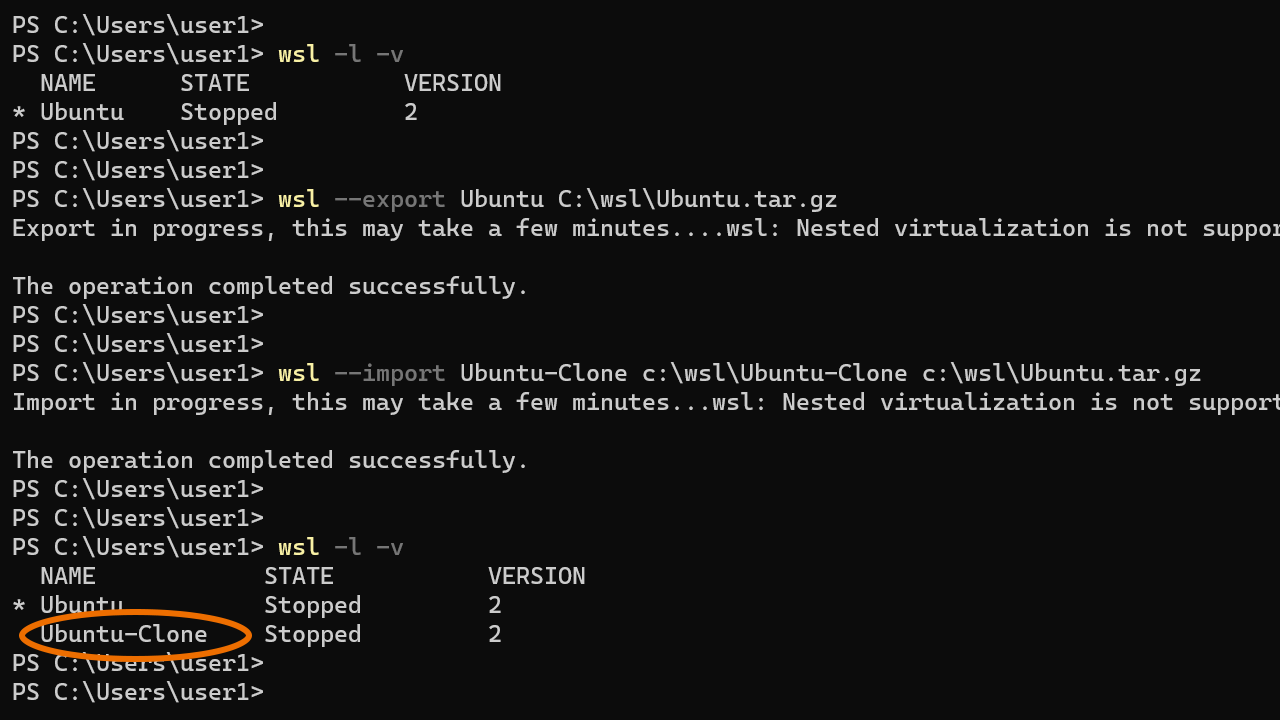
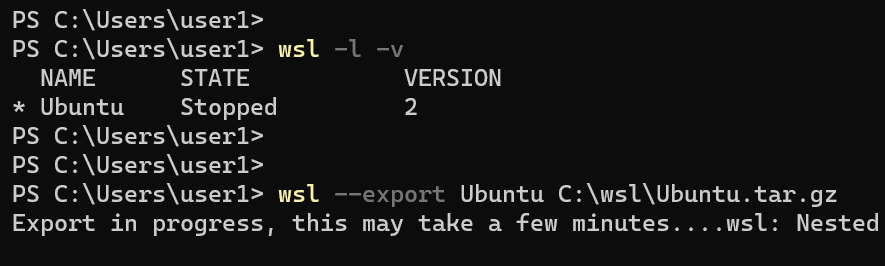
For example, the following command exports a distro named Ubuntu to a tar file called Ubuntu.tar.gz and saves it on the c:\wsl directory:
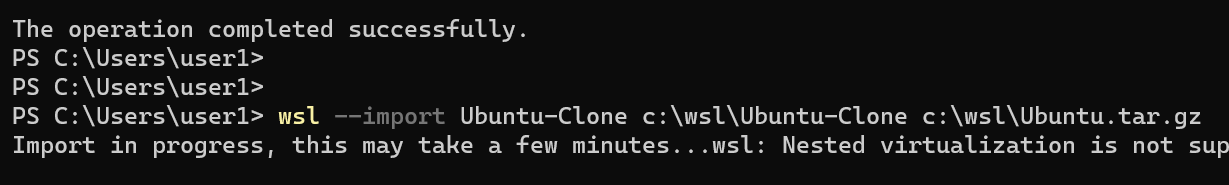
wsl --export Ubuntu C:\wsl\Ubuntu.tar.gzNow, to create a clone, we run the following command:
wsl --import Ubuntu-Clone c:\wsl\Ubuntu-Clone c:\wsl\Ubuntu.tar.gzThe above command creates a new distro called Ubuntu-Clone from the Ubuntu.tar.gz file. The new distro is installed on the C:\wsl directory.
And that's how we clone a Linux distribution in Windows Subsystem for Linux using the wsl --export and wsl --import commands.
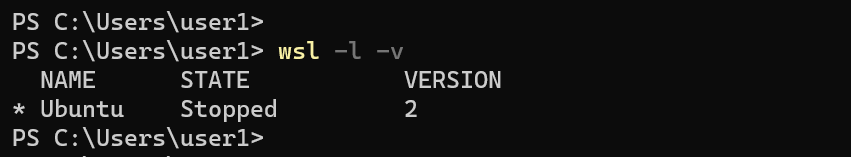
wsl --export to create a tar file backup of your WSL distribution.